RAG in Healthcare: The Complete Guide to AI-Powered Knowledge Management for Clinical Teams
Learn how RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) transforms healthcare knowledge management. Reduce documentation burden, eliminate policy conflicts, and enable instant clinical knowledge access.
Somewhere in your hospital right now, a nurse is scrolling through a shared drive looking for a policy that may or may not exist. Meanwhile, in another unit, a colleague is following a completely different version of that same procedure—one that was "passed by word of mouth" months ago but never documented.
This isn't a failure of your staff. It's a failure of how healthcare organizations manage knowledge.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) represents a fundamental shift in how clinical teams can access, maintain, and trust their institutional knowledge. Unlike traditional document management systems that require users to know what they're looking for (and where to find it), RAG-powered knowledge bases understand natural language queries and return accurate, source-cited answers from your actual documentation.
This guide covers everything clinical informatics teams need to understand: what RAG actually is, why it's different from generic AI chatbots, how it solves specific healthcare knowledge management problems, and what to consider when evaluating solutions.
What Is RAG and Why Does Healthcare Need It?
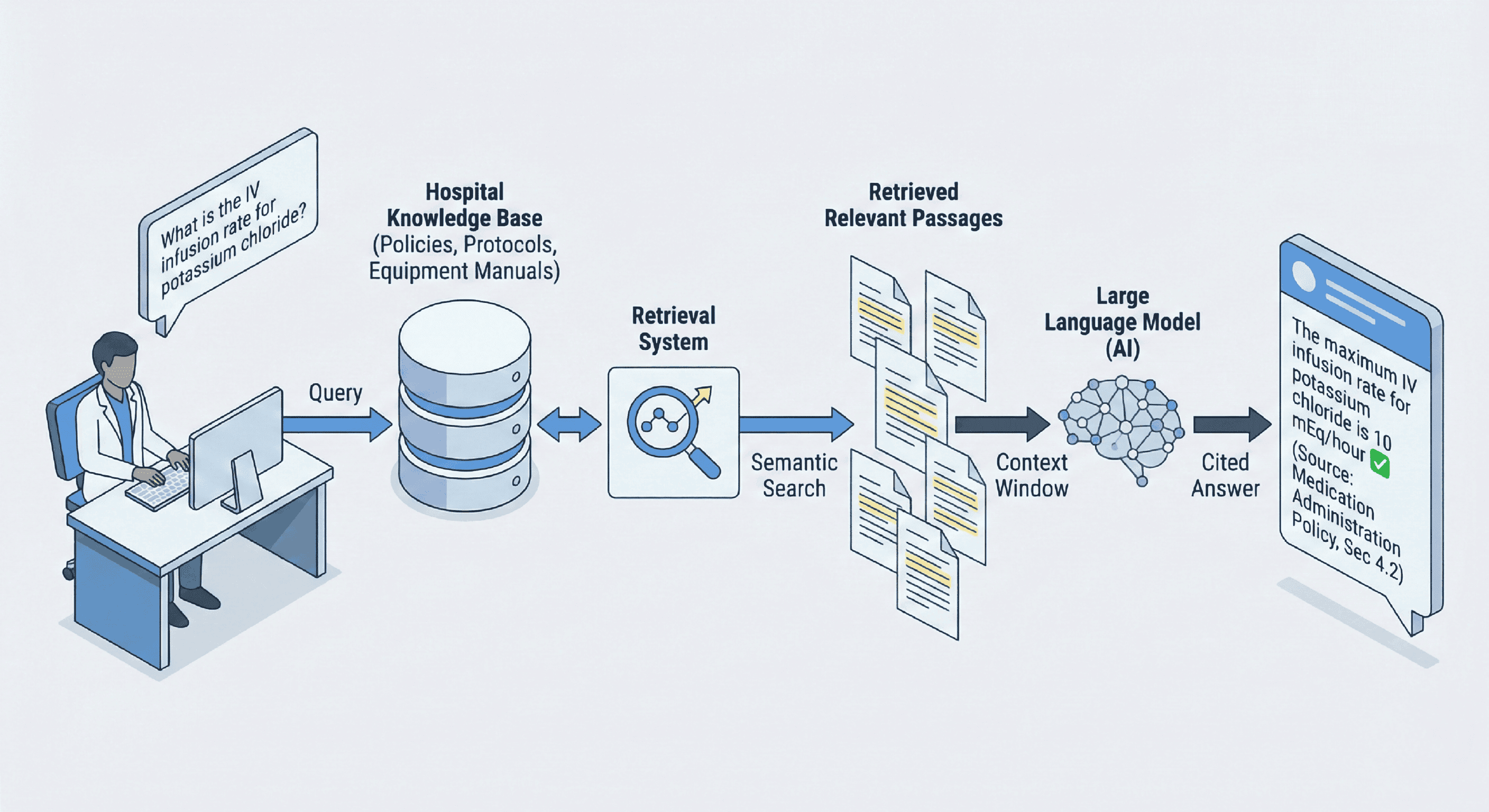
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It's an AI architecture that combines the natural language understanding of large language models with the precision of document retrieval. Instead of generating answers from a model's general training data (which leads to hallucinations and generic responses), RAG pulls information directly from your uploaded documents and generates responses grounded in that specific content.
Here's the critical distinction: when you ask ChatGPT about your hospital's medication reconciliation protocol, it gives you generic best practices. When you ask a RAG system configured with your actual protocols, it tells you exactly what your policy says—and shows you where in the document that answer came from.
The Healthcare Knowledge Crisis
Healthcare organizations generate and maintain massive documentation libraries:
- Policies and procedures spanning clinical, operational, and administrative functions
- Clinical protocols and guidelines that change as evidence evolves
- Regulatory compliance documentation for Joint Commission, CMS, state boards, and specialty accreditors
- Onboarding and training materials for continuous staff turnover
- Equipment manuals and maintenance documentation for thousands of devices
- Vendor contracts and supply specifications across procurement, pharmacy, and facilities
The problem isn't the existence of these documents. It's that nobody can find them when they need them.
Research from healthcare forums reveals the lived reality:
Nobody seems to know how to find most policies.
When you really want a policy to guide practice, there is none.
Each preceptor I was with had a 'different way' of doing things.
Multiple beliefs, passed by word of mouth, that people refer to as policies.
These aren't quotes from struggling facilities. This is the universal experience across healthcare—from academic medical centers to community hospitals to long-term care facilities.
What RAG Actually Solves
Traditional knowledge management approaches fail healthcare for predictable reasons:
| Traditional Approach | Why It Fails |
|---|---|
| Shared drives / folder hierarchies | Requires knowing where to look. Users give up after 3-4 clicks. |
| Intranet search | Keyword-based search returns too many irrelevant results or nothing at all. |
| Wiki platforms | Content sprawls, becomes stale, no clear ownership or maintenance. |
| Generic AI chatbots | Hallucinate answers not grounded in your actual policies. Dangerous for clinical use. |
RAG addresses these failures:
- Natural language queries — Staff ask questions in plain language ("What's our policy on restraint documentation?") instead of guessing keywords
- Source-grounded answers — Every response cites the specific document and section, so users can verify and trust the information
- No hallucinations — Responses are constrained to what's actually in your documents
- Universal document ingestion — PDFs (including scanned documents), Word files, spreadsheets, images with text—all become searchable
- Contextual understanding — The system understands synonyms, related concepts, and implicit questions
The Documentation Burden: Why This Matters Now
According to the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses, nurses spend approximately 40% of their 12-hour shifts on documentation—roughly 600-800 data points per shift, or one data point every 72 seconds. This isn't a minor inconvenience. Research published in PMC confirms it's the single largest driver of burnout and turnover in clinical staff.
But documentation burden isn't just about charting. It's the cumulative weight of:
- Searching for the correct form or template
- Verifying which fields are required versus optional
- Looking up the current version of a protocol before documenting against it
- Re-entering the same information across multiple systems
- Hunting for policy guidance when unusual situations arise
Studies consistently show that 16-34% of shift time is "preventable waste", time spent searching for information, equipment, or people that better systems would eliminate (BMJ Quality & Safety).
The Hidden Cost: Inconsistent Care
When policies are hard to find, staff do what any reasonable person does: they rely on memory, ask a colleague, or skip the lookup entirely.
This creates a dangerous pattern:
- Institutional knowledge becomes tribal — The "real" way to do things lives in experienced staff's heads, not in documentation
- Training becomes inconsistent — New nurses learn whatever their preceptor happens to know (or believe)
- Policy drift accelerates — Documented policies diverge from actual practice without anyone noticing
- Audit risk compounds — When surveyors ask for a policy, staff scramble to find the "official" version
The 18% first-year nursing turnover rate isn't just about workload (Empeon). It's about throwing new graduates into an environment where they can't reliably access the information they need to feel competent.
How RAG Transforms Clinical Knowledge Access
From Search to Ask
The fundamental shift with RAG is from searching to asking.
Traditional workflow:
- Open intranet
- Navigate to policies section
- Guess at folder structure (Clinical > Nursing > Medication Administration?)
- Try search with keywords
- Open 3-4 documents looking for the right one
- Read through document to find relevant section
- Hope it's the current version
RAG-enabled workflow:
- Ask: "What's the policy on IV infusion rate for potassium chloride?"
- Receive answer with direct citation to current policy
- Click source to verify if needed
The time savings are obvious. The risk reduction is harder to quantify but arguably more important.
Use Cases Across Healthcare Operations
Policy and Protocol Lookup
The most immediate application, and the one that resonates with every clinical staff member who's ever rage-quit a shared drive search.
Hospitals maintain hundreds (sometimes thousands) of policies across departments. The challenge isn't that policies don't exist—it's that staff can't find them when they need them. Different departments maintain their own versions. Folder structures require insider knowledge to navigate. Keyword search returns dozens of irrelevant results or nothing at all.
With RAG-powered knowledge access, the query shifts from "Where is the policy?" to "What does the policy say?"
Example queries:
- "What's our policy on family presence during resuscitation?"
- "Can an RN remove a chest tube, or does that require a physician?"
- "What's the documentation requirement for patient refusal of care?"
- "How do we handle medication administration for patients with known allergies?"
The system returns not just the answer, but the exact document and section—so staff can verify, cite, and trust the response.
Medication Information at Point of Care
Nurses and pharmacists report significant difficulty obtaining drug information quickly at the bedside (American Nurse Journal). Hospital drug protocols are often buried in systems designed for billing, not clinical workflow. Staff need dosing guidance, interaction checking, and contraindication warnings—without navigating three different applications.
A RAG-based medication knowledge base consolidates:
- Facility-specific formulary information
- IV compatibility and administration rates
- High-alert medication protocols
- Interaction warnings grounded in your actual patient population data
Example queries:
- "What's the maximum IV infusion rate for potassium chloride?"
- "Is vancomycin compatible with D5W in the same line?"
- "What monitoring is required after IV magnesium administration?"
- "What's our protocol for heparin dosing adjustment based on PTT?"
This isn't replacing clinical pharmacists—it's giving bedside nurses immediate access to the same information, reducing delays and workarounds.
Medical Equipment Documentation
Clinical staff struggle to find manuals, troubleshooting guides, and training materials for the equipment they use daily (PMC). Paper manuals get lost, contaminated, or damaged. Digital versions are scattered across vendor portals, shared drives, and someone's desktop folder from 2019.
Without a searchable repository, nurses delay procedures while trying to recall settings or find device operation guides. During emergencies, this delay matters.
A centralized, AI-searchable equipment knowledge base handles:
- Device operation guides and quick-start references
- Troubleshooting common alarms and error codes
- Maintenance schedules and calibration requirements
- Training materials for new staff or infrequently-used equipment
Example queries:
- "How do I clear the occlusion alarm on the Alaris pump?"
- "What's the setup procedure for BiPAP on the Philips Respironics?"
- "When was the last calibration due for the OR's electrosurgical units?"
- "What's the cleaning protocol for the portable ultrasound?"
Clinical Guidelines and Decision Support
Here's a uncomfortable truth: physicians rarely access clinical guidelines in practice. If they aren't aware of an update, they won't look for it. Busy clinicians rely on memory or experience rather than searching for the latest protocols (PMC).
Best practices languish unused—not because clinicians don't care, but because the friction of looking things up exceeds the perceived benefit.
RAG changes the calculus. When asking a question is as easy as typing it, clinicians actually ask.
Example queries:
- "What's the current sepsis bundle timing requirement?"
- "What are the updated stroke thrombolytic criteria?"
- "What's the evidence-based protocol for DKA management in pediatrics?"
- "When should we consider early goal-directed therapy?"
More advanced implementations can proactively surface relevant guidelines based on context—alerting staff to protocol updates in their specialty without requiring them to actively search.
Onboarding and New Hire Integration
New nurses are bombarded with policies, protocols, and documentation requirements in a compressed timeframe. The cognitive overload is real—and it contributes to the 18% of RNs who leave within their first year (PMC).
Traditional onboarding expects new hires to memorize hundreds of policies during orientation, then recall them perfectly under pressure. This doesn't work. Staff forget. They ask colleagues. They guess. They develop workarounds.
RAG-based onboarding shifts the model from "memorize everything" to "know how to ask." New staff learn they can query for answers in real-time, reducing anxiety and cognitive load.
Benefits for new hires:
- Instant answers to "how do we do X here?" questions
- Consistent information (no more conflicting advice from different preceptors)
- Reduced reliance on interrupting busy colleagues
- Confidence that they're following current policies, not outdated guidance
The system becomes a 24/7 preceptor that never gets frustrated, never gives conflicting answers, and always cites its sources.
Travel and Per Diem Nurse Integration
The challenge is even more acute for temporary staff. Travel nurses and per diem workers must learn new facility systems, protocols, and layouts repeatedly—often with minimal orientation time. Different facilities use different systems, different documentation requirements, different policies for the same procedures.
According to ShiftMed, this constant re-learning creates a significant burden on both the temporary staff and the permanent employees who must repeatedly answer the same orientation questions.
A facility-specific knowledge base that temporary staff can query immediately addresses:
- "Where is the crash cart on this unit?"
- "What's this facility's policy on verbal orders?"
- "Who do I contact for pharmacy questions after hours?"
- "What documentation is required for patient restraints here?"
The temporary nurse becomes productive faster. The permanent staff aren't interrupted as often. The facility reduces orientation costs.
Institutional Knowledge Preservation
Experienced staff embody tacit expertise that often isn't documented—device quirks, local protocols that evolved over time, the "real" way things work that nobody wrote down. When employees leave, that knowledge goes with them.
With approximately 18% annual nursing turnover (AMN Healthcare), losing seasoned clinicians directly erodes institutional knowledge. The problem compounds as the workforce ages—retirement waves are draining nursing wisdom faster than it can be transferred.
RAG platforms with knowledge capture workflows can:
- Convert verbal expertise into searchable documentation
- Preserve "tribal knowledge" before experienced staff retire
- Surface historical context for why certain procedures exist
- Maintain continuity through staffing transitions
Voice capture features are particularly valuable here—recording shift handoffs, debriefs, and informal teaching moments that would otherwise evaporate.
Compliance and HIPAA Knowledge Access
As we detailed in our analysis of why annual compliance training fails, 61% of healthcare employees fail computer safety rules assessments (StatPearls). Nearly half have witnessed impermissible PHI disclosure. There's a persistent gap between completing compliance training and actually retaining the knowledge.
Annual HIPAA training doesn't work because people forget. What works is just-in-time access to compliance guidance when situations arise.
Example queries:
- "Can I confirm a patient's appointment with their spouse who called?"
- "What are the rules for texting patient information to another provider?"
- "Can I access a coworker's medical record if they asked me to?"
- "What's required for a valid HIPAA authorization for research?"
A compliance knowledge base transforms HIPAA from an annual checkbox exercise into a practical resource staff actually use.
Audit and Accreditation Preparation
Regulatory surveys from Joint Commission, CMS, and state boards require swift retrieval of documentation. Hospitals scramble because records are scattered—missing signatures, conflicting versions, outdated policies that nobody archived properly.
The stress of audit preparation is familiar to anyone who's lived through it: surveyors ask for a policy, and staff frantically search while hoping the version they find is actually current.
RAG-based knowledge management addresses this by:
- Enabling instant retrieval of any policy by topic, not just filename
- Surfacing all related documentation for a given requirement
- Identifying version conflicts before auditors do
- Maintaining clear audit trails of document access and updates
Example queries:
- "Show me all policies related to infection control in the OR"
- "What's our current patient fall prevention protocol?"
- "When was the medication reconciliation policy last reviewed?"
- "What documentation supports our compliance with restraint requirements?"
The goal isn't just to survive audits—it's to make audit readiness a continuous state rather than a periodic panic.
Patient Portal Message Triage
Physicians receive 10+ remote patient contacts daily through patient portals (Practical Neurology). Messages are often non-urgent. Patients expect real-time responses. Time spent on portal responses is poorly reimbursed compared to phone calls.
The result: physician inbox overload, delayed responses, and staff burnout from a channel that was supposed to improve efficiency.
Patient-facing RAG chatbots can triage queries before they reach clinical staff:
- Answering common questions from existing patient education materials
- Directing urgent concerns to appropriate channels
- Providing appointment and prescription information
- Reducing the volume of messages requiring physician response
This isn't AI practicing medicine—it's AI handling the routine queries that consume physician time without requiring clinical judgment.
Patient Education Materials
Nurses spend significant time searching for condition-specific handouts or discharge instructions. Barriers include lack of suitable resources, inconsistent quality, and the challenge of finding materials in languages other than English (PMC).
Smaller hospitals leave nurses to cobble together printouts from various sources. Larger systems have materials, but staff can't find them when they need them.
A searchable patient education library with AI-powered lookup enables:
- "What discharge instructions do we have for new diabetes diagnosis?"
- "Is there a patient handout for colonoscopy prep in Spanish?"
- "What's our pediatric asthma action plan template?"
- "Do we have patient-friendly information about warfarin interactions?"
Better access to education materials improves patient outcomes and reduces readmission risk—while saving nurses the time they'd otherwise spend hunting through folders.
Vendor and Contract Documentation
Non-clinical documentation is often the forgotten stepchild of knowledge management. Vendor contracts, supply specifications, formulary agreements—these documents are scattered across departments. Finance has equipment contracts in PDFs, pharmacists have benefit documents, procurement stores specs separately.
When staff need to confirm pricing, verify specifications, or check contract terms, they email multiple people and wait. The information exists; it's just inaccessible.
A unified operational knowledge base handles:
- "What's the contracted price for surgical gloves from Cardinal?"
- "What's the warranty status on the MRI equipment?"
- "When does our pharmacy wholesaler agreement expire?"
- "What are the lead times for our backup ventilator supplier?"
This isn't glamorous work, but the operational efficiency gains are real.
Beyond Search: AI-Powered Knowledge Maintenance
Here's where advanced agentic RAG platforms differentiate from traditional document management: the ability to not just retrieve information, but to actively maintain knowledge base integrity.
The Contradiction Problem
Large healthcare organizations accumulate documentation over years (sometimes decades) across departments that don't coordinate. The result is predictable:
- Conflicting policies — The nursing policy says one thing; the pharmacy policy says another
- Outdated references — Documents cite procedures, systems, or even employees that no longer exist
- Version chaos — Multiple versions of the "same" policy exist in different locations
- Superseded guidance — Clinical protocols reference outdated evidence or guidelines
Staff working in this environment develop a rational distrust of documentation. They stop looking things up because they can't trust what they find.
Automated Contradiction Detection
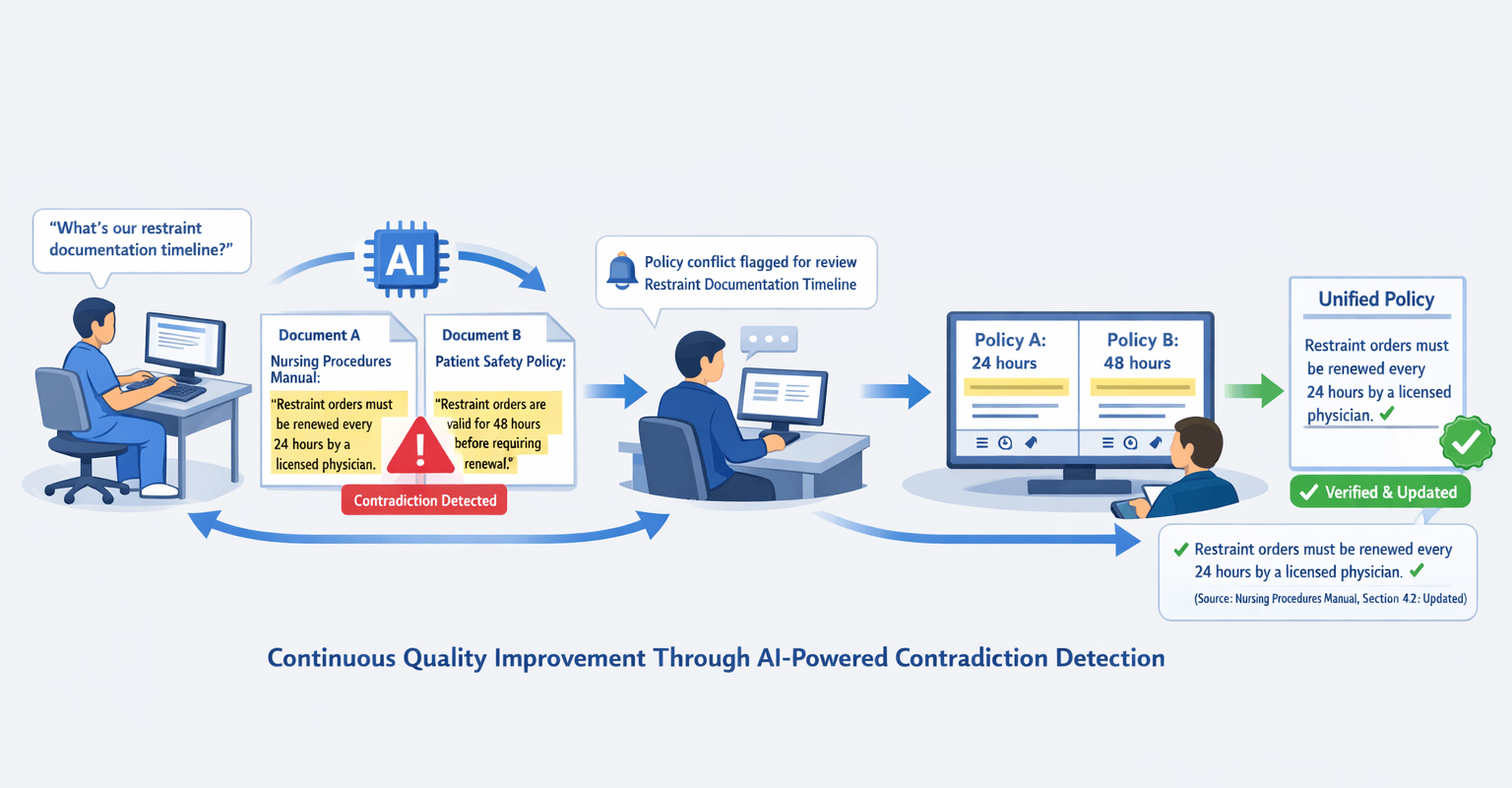
Advanced agentic AI systems with RAG and the right tools can analyze your entire document library and identify:
- Direct contradictions — Policy A says 24 hours; Policy B says 48 hours for the same process
- Implicit conflicts — Workflow descriptions that assume different underlying procedures
- Outdated references — Mentions of former employees, discontinued systems, or superseded regulations
- Missing documentation — Processes referenced but never actually documented
This isn't a feature that exists in traditional document management. SharePoint can't tell you that two of your policies contradict each other. Neither can Confluence, Google Drive, or any folder-based system.
Feedback-Driven Quality Improvement
Some RAG platforms enable a feedback loop where user interactions drive documentation improvements:
- Staff member asks a question
- System provides an answer from documentation
- User marks answer as unhelpful or incorrect
- System flags the source document for review
- Documentation team investigates and corrects
- Future queries return accurate information
This transforms the knowledge base from a static repository into a self-improving system. Bad experiences become signals that drive quality improvements.
Implementation Considerations for Healthcare
Document Ingestion Challenges
Healthcare documentation presents unique technical challenges:
Scanned documents and legacy PDFs
Many hospitals have policy libraries that include scanned documents from years of paper-based systems. Basic OCR often fails on:
- Low-quality scans
- Multi-column layouts
- Tables and forms
- Handwritten annotations
Enterprise RAG platforms need robust hybrid parsing that can handle these documents accurately—or your knowledge base will have significant gaps.
Format diversity
Clinical documentation exists in:
- PDFs (native and scanned)
- Word documents
- Excel spreadsheets (formularies, schedules, specifications)
- PowerPoint presentations (training materials)
- Images with embedded text
- Legacy formats from retired systems
The system must handle all of these without manual conversion.
HIPAA and Security Considerations
RAG systems for healthcare must address:
- Data residency — Where is your documentation stored? Where does AI processing occur?
- Access controls — Can the system enforce role-based access to sensitive documentation?
- Audit trails — Can you demonstrate who accessed what information and when?
- PHI handling — While policy documents typically don't contain PHI, some clinical documentation might. How does the system handle this?
- Model training — Does your data train the underlying AI model? For most healthcare use cases, it should not.
Reputable vendors will have BAA (Business Associate Agreement) frameworks and SOC 2 compliance at minimum.
Integration Requirements
Consider how a RAG system fits into existing infrastructure:
- Single Sign-On (SSO) — Integration with hospital identity management
- Intranet embedding — Can the chat interface be embedded in existing portals?
- Mobile access — Clinical staff often work from tablets and phones
- EHR adjacency — While direct EHR integration is complex, being accessible alongside EHR workflows matters
Change Management Reality
Technology is the easy part. The harder challenge is changing how staff interact with institutional knowledge.
Successful implementations typically:
- Start with high-pain use cases — Pick problems staff are already frustrated about (policy lookup, new hire questions)
- Train champions in each unit — Peer-to-peer advocacy drives adoption better than top-down mandates
- Make it easier than alternatives — If asking the system isn't faster than asking a colleague, staff won't use it
- Surface visible wins — When the system prevents an error or saves significant time, communicate that broadly
- Close the feedback loop — Show staff that their feedback actually improves the system
Evaluating RAG Solutions for Healthcare
Not all RAG platforms are created equal. Healthcare organizations should evaluate:
Core Capabilities
| Capability | Why It Matters | Questions to Ask |
|---|---|---|
| Document parsing quality | Poor parsing = unreliable answers | How does it handle scanned PDFs? Multi-column layouts? |
| Source attribution | Staff need to verify answers | Does every answer cite specific documents and sections? |
| Update freshness | Outdated answers are dangerous | How quickly are document updates reflected in responses? |
| Access controls | Not all documents are for all users | Can different roles access different document sets? |
Differentiating Features
| Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Contradiction detection | Proactively identifies policy conflicts before they cause problems |
| Outdated content flagging | Surfaces documents that need review before auditors find them |
| Feedback-driven improvement | User signals drive automatic quality improvements |
| Embeddable agents | Deploy knowledge access to patient portals, staff apps, specific departments |
| Voice capture | Convert verbal knowledge (shift handoffs, debriefs) into searchable content |
Red Flags
Watch out for:
- Generic AI claims — "AI-powered" without explanation of how responses are grounded in your documents
- No source citation — If you can't see where answers come from, you can't trust them
- Cloud-only storage without HIPAA controls — Appropriate for consumer products, not healthcare
- Vendor lock-in — Can you export your documents and any created metadata?
- Feature complexity over usability — The best system is the one staff will actually use
The Bigger Picture: Knowledge as Infrastructure
Healthcare has systematically underinvested in knowledge infrastructure while over-investing in transactional systems.
EHRs capture what happened to patients. Revenue cycle systems capture what was billed. Supply chain systems track what was consumed.
But the institutional knowledge that guides how staff should do their work? That's still fragmented across shared drives, wiki pages, three-ring binders, and the memories of experienced clinicians who are increasingly leaving the workforce.
RAG-based knowledge management isn't just another IT system. It's the infrastructure layer that makes all other systems more effective—because it ensures staff can actually find and trust the information they need to do their jobs correctly.
The Stakes
- 40% of nursing shift time spent on documentation (AACN)
- 16-34% of shift time identified as preventable waste (BMJ Quality & Safety)
- 18% first-year nursing turnover rate (Empeon)
- 61% of healthcare employees fail computer safety rules assessment (StatPearls)
- 60% of SNF Medicare denials attributed to insufficient documentation (Sweeney Law Firm)
These aren't technology problems. They're knowledge access problems that technology can solve—if implemented correctly.
Getting Started
For clinical informatics teams evaluating RAG solutions:
1. Audit your current state
- Where does documentation actually live? (Often more locations than anyone realizes)
- What are the most common knowledge-seeking tasks that frustrate staff?
- Which policies or protocols generate the most questions?
2. Define success metrics
- Time to find specific policies
- Staff satisfaction with information access
- Audit preparation time
- New hire time-to-competency
3. Start small, prove value
- Begin with a single high-pain use case (policy lookup, onboarding)
- Demonstrate measurable improvement
- Expand based on evidence
4. Evaluate vendors critically
- Request demo with your actual documents (scanned PDFs, messy Word files)
- Test edge cases and failure modes
- Verify security and compliance claims independently
The technology exists today to transform how healthcare organizations manage institutional knowledge. The question isn't whether RAG-based systems will become standard in healthcare—it's which organizations will capture the benefits first.
Frequently Asked Questions
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is an AI architecture that combines document retrieval with natural language generation to provide accurate, source-cited answers from healthcare organization's actual documentation—including policies, protocols, guidelines, and operational documents.
Generic AI models like ChatGPT generate responses from general training data and can hallucinate plausible-sounding but incorrect information. RAG systems constrain responses to your specific uploaded documents and cite exact sources, making them appropriate for clinical use where accuracy is critical.
RAG technology itself is neutral—compliance depends on the specific vendor implementation. Healthcare organizations should verify data residency, access controls, audit capabilities, and BAA availability before implementation.
Initial deployment can occur within weeks for limited use cases (policy lookup, FAQ support). Full organizational deployment with change management typically takes 3-6 months depending on documentation volume and integration requirements.
Enterprise RAG platforms handle PDFs (including scanned documents), Word files, Excel spreadsheets, PowerPoint presentations, and images with text. The quality of handling varies by vendor—always test with representative samples of your actual documentation.